Callback과 Promise와 async await로 비동기 작성하기

요약
Callback, Promise, async await 모두 비동기를 처리하는 방법이다.
콜백함수는 콜백 지옥과 같은 문제점이 있다.
Promise를 사용하면 흐름을 이해하긴 좋지만, then 지옥이 나타날 수 있다.
async await로 Promise객체를 더 쉽게 사용할 수 있다. try-catch로 에러처리를 해야한다.
비동기 처리가 무엇인지 부터!
특정 코드의 실행을 완료할 때 까지 기다리지 않고 다른 코드를 먼저 수행하는 것이다. 자바스크립트에서는 콜백함수, Promise, async await문법으로 비동기를 다룰 수 있다.
자바스크립트의 비동기 동작원리.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8aGhZQkoFbQ
Callback을 사용한 비동기 처리
우선 가장 기본이 되는 콜백 함수를 알아보자!
callback 함수란?
- 다른 함수의 인자로써 이용되는 함수.
- 어떤 이벤트에 의해 호출되어지는 함수.
- 특정 작업이 완료된 후에 실행되도록 전달되는 함수.
위의 용도로 사용된다.
function asyncCallback(callback) {
// 1. callback = 다른 함수의 인자로써 이용되는 함수.
setTimeout(() => {
// 2. 어떤 이벤트(setTimeout)에 의해 호출되어지는 함수.
callback('1초 지남');
}, 1000);
}
function message(msg) {
console.log(msg); // 받은 인자를 콘솔에 출력합니다.
}
asyncCallback(message);콜백지옥이란?
비동기 작업을 위해 사용되는 콜백의 특성상, 비동기 이후에 처리될 작업들을 콜백 내부에 작성해야 합니다. 무심하게 짜면 아래와 같은 코드가 발생하게 되며, 읽기 어렵고 복잡합니다.
asyncCallback(function (result1) {
message(result1);
asyncCallback(function (result2) {
message(result2);
asyncCallback(function (result3) {
message(result3);
// 계속해서 중첩될 수 있음...
});
});
});Promise을 사용한 비동기 처리 예제
이런 콜백함수의 문제를 보완할 방법이 있다. Promise객체를 사용하는 방법이다. Promise객체를 사용하면 아래와 같이 흐름을 보기 좋게 만들 수 있다.
function asyncPromise() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('1초 지남');
}, 1000); // 1초 동안 대기
});
}
asyncPromise()
.then((result1) => {
message(result1);
return asyncPromise(); // 다음 프로미스 반환
})
.then((result2) => {
message(result2);
return asyncPromise(); // 다음 프로미스 반환
})
.then((result3) => {
message(result3);
// 필요한 경우 여기서 계속 체인을 이어갈 수 있습니다.
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('Error:', error);
});자! 만약 더 보기 좋다면 프로미스 객체에 대해 더 깊게 알아보자.
Promise란?
일단 정의부터 슬쩍 요약해보면 JavaScript에서 비동기에 사용하는 객체이다.
"A promise is an object that may produce a single value some time in the future"
프로미스는 자바스크립트 비동기 처리에 사용되는 객체이다. 비동기 처리란 '특정 코드의 실행이 완료될 때까지 기다리지 않고 다음 코드를 먼저 수행하는 자바스크립트의 특성'이다.
Promise예제
// key에 True를 할당하면 wait 1 sec가 실행되고, False를 할당하면 'Error!'가 실행된다.
function asyncPromise(key) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (key === true) {
resolve('waited 1 sec.') // resolve를 만나면 Promise객체에 성공을 저장한다.
};
else {
reject(new Error('Error!')) // reject를 만나면 Promise객체에 Error객체를 저장한다.
};
}, 1000);
});
}
asyncPromise(true)
.then((result) => {
// resolve를 만나면 then함수를 실행시킨다.
console.log(result);
})
.catch((error) => {
// reject를 만나면 then함수를 건너뛰고 catch를 실행시킨다.
console.log(error);
});Promise 객체의 인자를 보면 다음과 같다.
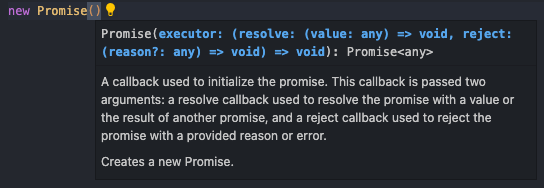
resolve와 reject라는 이름의 내장 콜백함수를 가진다.
한 줄로 요약하면 성공했을 때 resolve를 실행시키고, 실패했을 땐 reject는 실행하면 된다.
성공했을 경우를 위의 예제를 통해 설명해보면,
async(true)를 실행시키면,resolve('waited 1 sec.')가 실행되어 return Promise 객체에 성공을 저장해 반환한다.- 후에 뒤에 붙어있는
.then()을 실행시킨다..then()은 Promise.prototype.then()이다. - 이렇게 프로미스 객체를
Promise.prototype.then()을 통해 계~~~속 이을 수 있다.
실패했을 경우를 위의 예제를 통해 설명해보면,
async(false)를 실행시키면,reject(new Error('Error!'))가 실행되어 return Promise 객체에 실패가 저장된다.- 프로미스 객체가 실패를 만나면,
.then()을 건너뛰고.catch()가 실행된다.
어렵죠? 저도 설명하기 되게 어렵네요...... 또한 finally문법도 지원합니다.
finally
finally메소드는 Promise의 성공과 실패에 관계없이 처리만 되면 실행되는 함수이다. 그러니까 finally를 사용하면 무조건!!! 실행된다!!!
const successPromise = new Promise(...);
successPromise
.then((value) => `${value} is`)
.then((secondValue) => {
throw new Error("Error!!");
}) // 에러 발생
.then((thirdValue) => console.log("possible"))
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
})
.finally(() => console.log("chain end"));
// 위 Promise상태가 어떻든 간에 Promise 객체가 반환되었기 때문에 finally 메소드가 무조건적으로 실행 됨.하지만, 결국 또 지옥
.then()들이 복잡하게 얽힐 수 도 있다. 아래 예제는 좀 처참한 예제이지만, 이렇게 될 수도 있다!
doSomething()
.then((result) => {
return doSomethingElse(result)
.then((newResult) => {
return doThirdThing(newResult)
.then((finalResult) => {
console.log(`Got the final result: ${finalResult}`);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(`Error in doThirdThing: ${error}`);
});
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(`Error in doSomethingElse: ${error}`);
});
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(`Error in doSomething: ${error}`);
});async await
async await를 사용하면 Promise를 편리하게 사용할 수 있다.
비동기 처리방식 중 하나인 Generator (제너레이터에 대한 설명:제로초 블로그)의 문제를 효과적으로 해결할 수 있는 ES2017(ES8)에 나온 최신 문법이므로 사용해보자!
async function
function 앞에 async를 붙이면 해당 함수는 항상 Promise객체를 반환한다.
async function 안에 await를 붙이면 해당 함수는 항상 Promise객체를 반환한다.
그러니까 main, f1, f2, f3모두 Promise객체를 반환한다.
async function main() {
const result1 = await f1(); // f1이 일반 값을 반환해도 Promise로 감싸져 동작함
console.log(result1)
const result2 = await f2(); // f2도 일반 값을 반환해도 Promise로 감싸져 동작함
console.log(result2)
const result3 = await f3(); // 마찬가지로 f3도 일반 값을 반환해도 Promise로 감싸져 동작함
console.log(result3)
return 1;
}
main().then(...); // main도 Promise객체를 반환하므로 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다.이렇게! 비동기 처리를 하는 Promise객체를 async, await키워드로 편하게 사용할 수 있다.
사용 방법
async 함수 안에서 await를 만나면 해당함수가 return 될 때까지 기다린다. 그 뒤에 이어서 실행한다.
async function main() {
const result1 = await f1(); // f1의 반환을 기다린 후 result1에 저장.
console.log(result1) // 출력
const result2 = await f2(); // f2의 반환을 기다린 후 result2에 저장.
console.log(result2) // 출력
const result3 = await f3(); // 마찬가지로 f3의 반환을 기다린 후 result3에 저장.
console.log(result3) // 출력
return 1;
}
main().then(...); // main도 Promise객체를 반환하므로 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다.위에서 사용했던 .then을 사용한 예제와 async await를 사용한 예제를 확인해봅시다.
기본 Promise예제와 async await예제 비교하기
두 예제를 보고, 상황에 따라 좋은 방법으로 해결하자!
Promise만 사용한 예제
function message(msg) {
console.log(msg); // 받은 인자를 콘솔에 출력합니다.
}
function asyncPromise() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('1초 지남');
}, 1000); // 1초 동안 대기
});
}
asyncPromise()
.then((result1) => {
message(result1);
return asyncPromise(); // 다음 프로미스 반환
})
.then((result2) => {
message(result2);
return asyncPromise(); // 다음 프로미스 반환
})
.then((result3) => {
message(result3);
// 필요한 경우 여기서 계속 체인을 이어갈 수 있습니다.
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('Error:', error);
});async await 예제
function message(msg) {
console.log(msg); // 받은 인자를 콘솔에 출력합니다.
}
function asyncPromise() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("1초 지남");
}, 1000); // 1초 동안 대기
});
}
async function runAsync() {
try {
const result1 = await asyncPromise(); // 1초 기다렸다가 결과값을 result1에 저장합니다.
message(result1);
const result2 = await asyncPromise(); // 1초 기다렸다가 결과값을 result2에 저장합니다.
message(result2);
const result3 = await asyncPromise(); // 1초 기다렸다가 결과값을 result3에 저장합니다.
message(result3);
// 필요한 경우 여기서 계속 체인을 이어갈 수 있습니다.
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error);
}
}
runAsync();async await의 에러핸들링
async await의 경우 .catch()와 같이 에러를 처리하는 특수한 방법이 없습니다. 그래서 try-catch문을 사용해야 합니다.
예시:
async function runAsync() {
try {
const result1 = await asyncPromise(); // 에러를 만나면 catch가 실행됩니다.
message(result1);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error);
}
}
runAsync();아래와 같은 코드처럼, try-catch를 사용하지 않고 에러를 반환하게 되면, 함수f()의 return이 실패상태의 Promise가 되어 Promise오류를 발생시킵니다.
async function f() {
let response = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject("에러");
});
}
// f()는 거부 상태의 프라미스가 됩니다.
f() // 에러를 처리하지 않으면, 콘솔에 오류메세지를 출력합니다.
f().catch(alert); // 오류메세지가 없는 alert를 띄웁니다.마무리
callback함수, Promise객체, async await를 알아보았습니다.
여전히 모두 쓰이고 있고, 상황에 맞는! 비동기 처리방식을! 작성합니다!
레퍼런스
- https://velog.io/@wngud4950/%ED%94%84%EB%A1%9C%EB%AF%B8%EC%8A%A4Promise%EB%9E%80-%EC%BD%9C%EB%B0%B1%ED%95%A8%EC%88%98%EC%99%80%EC%9D%98-%EC%B0%A8%EC%9D%B4%EC%A0%90
- https://danbom425.tistory.com/34
- https://jcon.tistory.com/189
- https://ko.javascript.info/async-await
- https://ko.javascript.info/promise-basics
- https://www.zerocho.com/category/EcmaScript/post/579b34e3062e76a002648af5